Q 1) Why Java is not 100% Object-oriented?
Ans) Because of Primitive data types namely:
Boolean, byte, char, int, float, double, long, short.
To make them Object Oriented we have rapper classes which actually “wrap” the primitive data type into an object of that class.
Q 2) Why pointers are not used in Java?
Ans) 1. They are unsafe.
2) Increases the complexity of the program and since Java is known for its simplicity of code, adding the concept of pointers will be contradicting.
3) Since JVM is responsible for implicit memory allocation, thus in order to avoid direct access to memory by the user, pointers are discouraged in Java.
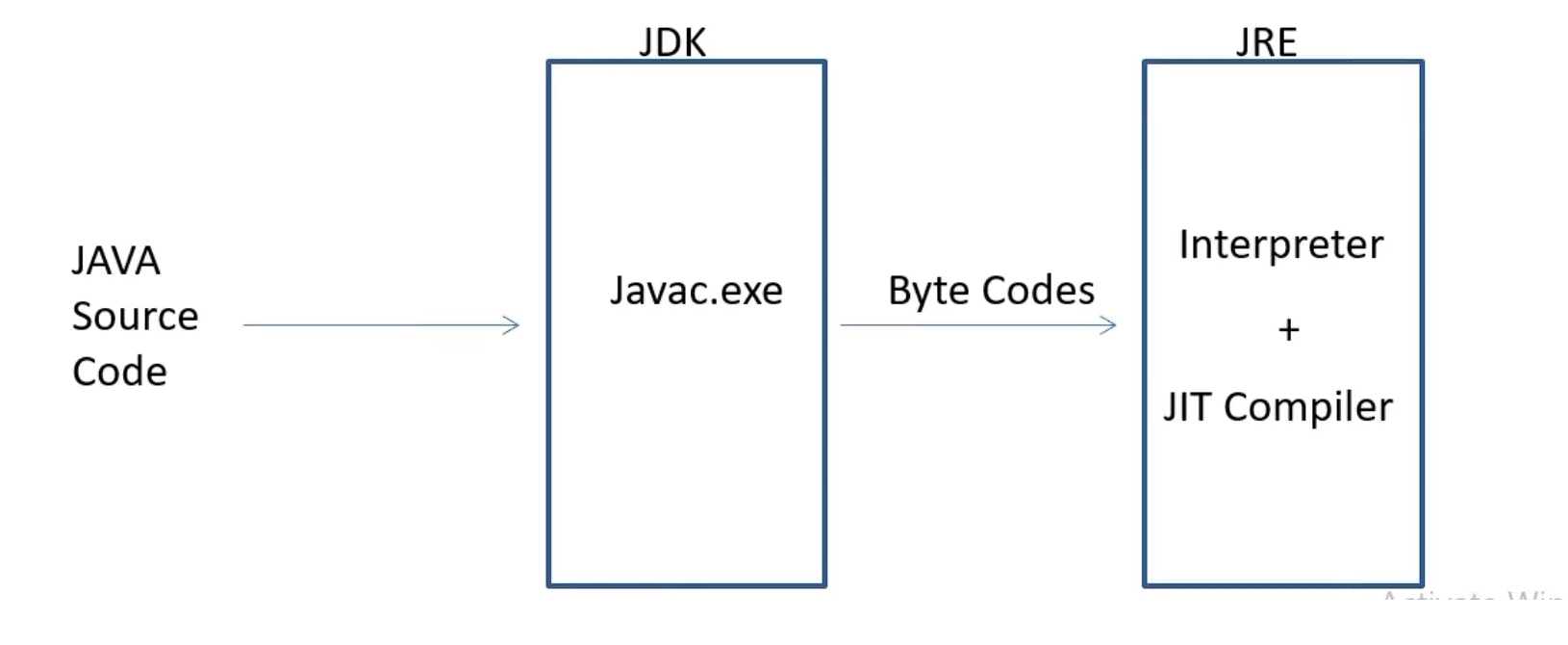
Q3) What is JIT compiler in Java?
Ans) The JIT or Just-In-Time compiler is a crucial component of the JRE (Java Runtime Environment), which is in charge of performance optimisation of Java-based programmes during run time. For both the end-user and the application developer, the compiler is one of the crucial factors in determining how well an application performs.
Q 4) Why String is immutable in java?
Ans: 1)String pool requires the string to be immutable otherwise shared reference can be Changed from anywhere.
2) security because string is shared on different area like file system, networking connection, database connection , having immutable string allows you to be secure and safe because no one can change reference of string once it gets created.
Q5) What is a marker interface?
Ans: A marker interface can be defined as the interface having no data member and member
functions. In simpler terms, an empty interface is called the Marker interface.
e.g. Serializable, Cloneable
Q6 ) Can you override a private or static method in Java?
Ans: 1) you can not override a private or static method in Java.
2) you cannot override a private method in the sub class because it’s not accessible there, what you do is create another private method with the same name in the child class.
3) For static methods if you create a similar method with same return type and same method arguments in the child class then it will hide the superclass method, this is known as
method hiding.
Q7) Does”finally” always execute in Java?
Ans: Not in the following cases
1) “System.exit()” function
2) system crash
Q8) What Methods Does the Object Class Have?
Ans:) Java.lang.Object class, parent of all has following methods :
- protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException : Creates and returns a copy of this object.
- public boolean equals(Object obj) : Indicates whether some other object is “equal to” this one.
- protected void finalize() throws Throwable : Called by the garbage collector on an object when garbagecöllection determines that there are no more references to the object.
- public final Class getClass() : Returns the runtime class of an object.
- public int hashCode(): Returns a hash code value for the object.
- public String toString(): Returns a string representation of the object.
- public final void notify()
- public final void notifyAll()
- public final void wait()
- public final void wait(long timeout)
- public final void wait(long timeout, int nanos)
Q9) How Can You Make a Class Immutable?
Ans 🙂 Below are the steps:
- Declare the class as final so it can’t be extended.
- Make all fields private so that direct access is not allowed.
- Don’t provide setter methods for variables
- Make all mutable fields final so that it’s value can be assigned only once.
- Initialize all the fields via a constructor performing a deep copy.
- Perform cloning of objects in the getter methods to return a copy rather than returning the actual object reference.

